Neutron experiments assisted expose the one-carbon enzymatic system that manufactures crucial food sources for cancer cells that depend upon vitamin B6, offering crucial insights into creating unique drugs to slow the spread of aggressive cancers. Credit: Jill Hemman/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are advancing cancer treatment research study by developing drugs that target the metabolic paths cancer cells depend on for development. By mapping the structure of an essential enzyme with neutrons and X-rays, they intend to establish treatments for aggressive cancers, consisting of lung and breast cancer.
After an extremely admired research study project that effectively upgraded a liver disease C drug into among the leading drug treatments for
Amino acids are a set of organic compounds used to build proteins. There are about 500 naturally occurring known amino acids, though only 20 appear in the genetic code. Proteins consist of one or more chains of amino acids called polypeptides. The sequence of the amino acid chain causes the polypeptide to fold into a shape that is biologically active. The amino acid sequences of proteins are encoded in the genes. Nine proteinogenic amino acids are called “essential” for humans because they cannot be produced from other compounds by the human body and so must be taken in as food.
” data-gt-translate-attributes=” L_SQUARE_B.L_SQUARE_B.”attribute”:”data-cmtooltip “,”format”:”html[19459026R_SQUARE_BR_SQUARE_B”tabindex=”0″role=”link”>aminoacidsDNA and RNATo put it simply, 1C systems resemble fuel sources that cells require to grow and increase. That likewise suggests they’re important for the unmanageable expansion of cancer cells.
“This research study is intriguing because the particles we’re preparing to create would be metabolic drugs, which were a few of the very first drugs– like methotrexate– that were established to deal with cancer. For many years, research study has actually entered other instructions to study other paths, “stated Kovalevsky.”But just recently there’s been a reignition, or return, to the metabolic drugs due to the fact that you actually require a plethora of various intervention choices, in some cases at the exact same time to fight all the various kinds of cancer.”
Pioneering Drug Design With Neutron Scattering
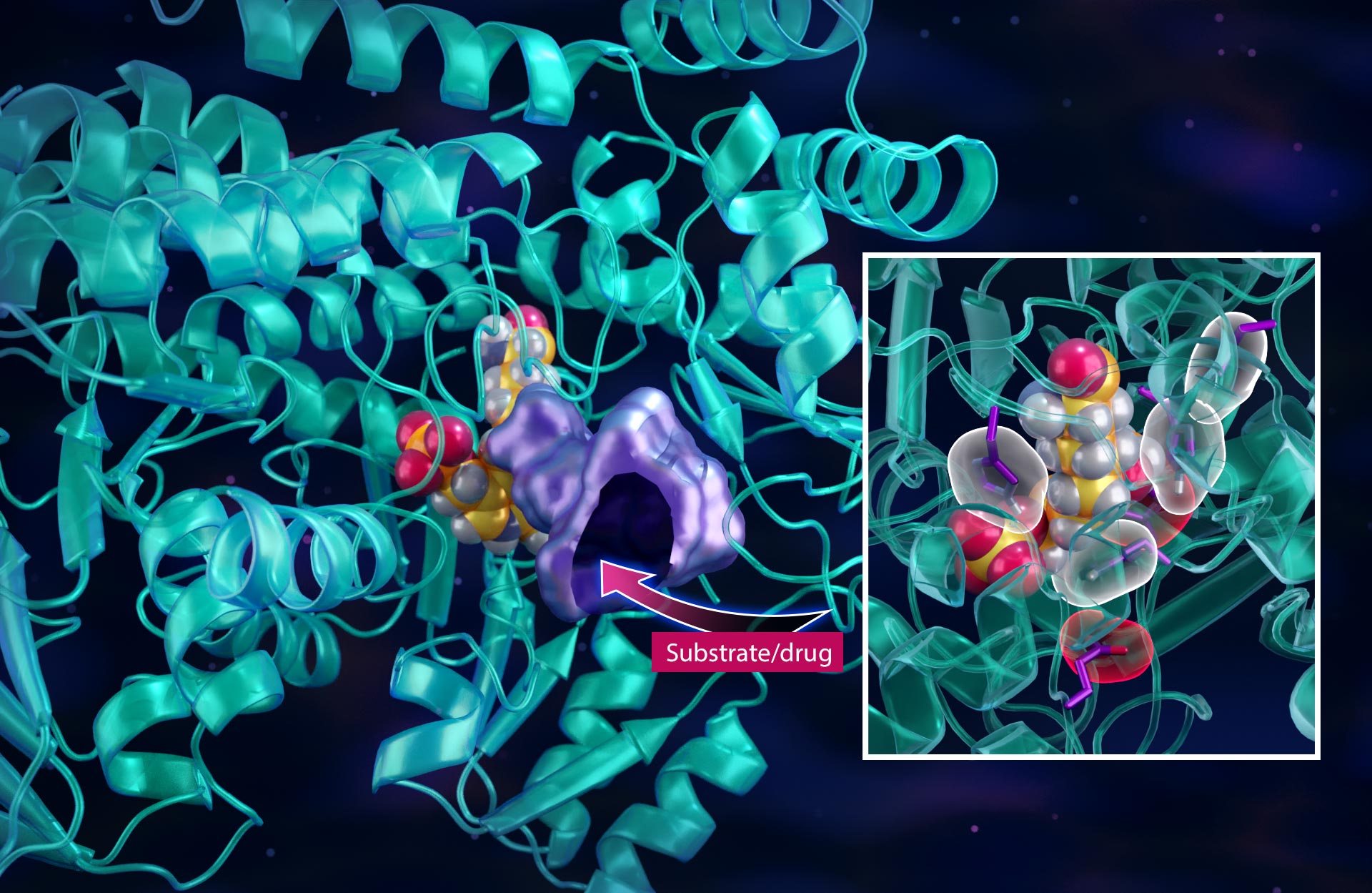
Among the essential enzymes within the 1C path is serine hydroxymethyltransferase, or SHMT. SHMT is accountable for starting the lion’s share of 1C responses for the cell. And, presently, no authorized anti-cancer drugs exist that target SHMT particularly.
“The 1C metabolic process path is’pirated’by lots of kinds of cancer. If you consider this path as a highway, SHMT is the on-ramp cancer requires to pirate traffic,” stated postdoctoral scientist Victoria Drago, the research study’s lead author.”Blocking the enzyme with inhibitors or’ obstructions ‘avoids cancer cells from utilizing the highway, successfully cutting off their fuel supply, thus avoiding them from spreading out. “
Creating a drug needs an in-depth understanding of the enzyme structure and how the structure underpins its function at the atomic level. For this, the group utilized a mix of neutron and x-ray scattering experiments to map the area of every atom in the enzyme structure in addition to the network of chemical bonds and the matching electrical charges.
Understanding how little particles connect to the enzyme is the crucial to developing matching drug particles– like creating puzzle pieces in 3D– however the pieces not just need to match fit however likewise in electrical charge. Kovalevsky compared it to utilizing the ideal battery with the appropriate size and orientation to power particular electronic gadgets.
In contrast to x-rays, which are more conscious heavy components such as carbon, neutrons are perfect for studying light components such as hydrogen and work in figuring out the electrical charges and mapping the enzyme-drug interactions.
Neutrons are specifically essential because hydrogen atoms comprise roughly 50% of all atoms in biological systems, and their existence likewise plays a considerable function in identifying the strength of chemical bonds in between a drug particle and an enzyme.
To track the hydrogen atoms, the scientists utilized the neutron instruments MANDI and IMAGINE at ORNL’s Spallation Neutron Source, or SNS, and High Flux Isotope Reactor, or HFIR. The neutron experiments enabled the group to observe how the SHMT enzyme binds its physiological particle– serine amino DOI: 10.1038/ s42004-023-00964-9
In addition to Kovalevsky and Drago, the research study’s coauthors consist of Claudia Campos, Mattea Hooper, Aliyah Collins, Oksana Gerlits, Kevin L. Weiss, Matthew P. Blakeley and Robert S. Phillips. Complementary neutron and x-ray measurements were carried out at the Institut Laue-Langevin, France, and the Advanced Photon Source, or APS, at Argonne National Laboratory.
HFIR, SNS, and APS are DOE Office of Science user centers.