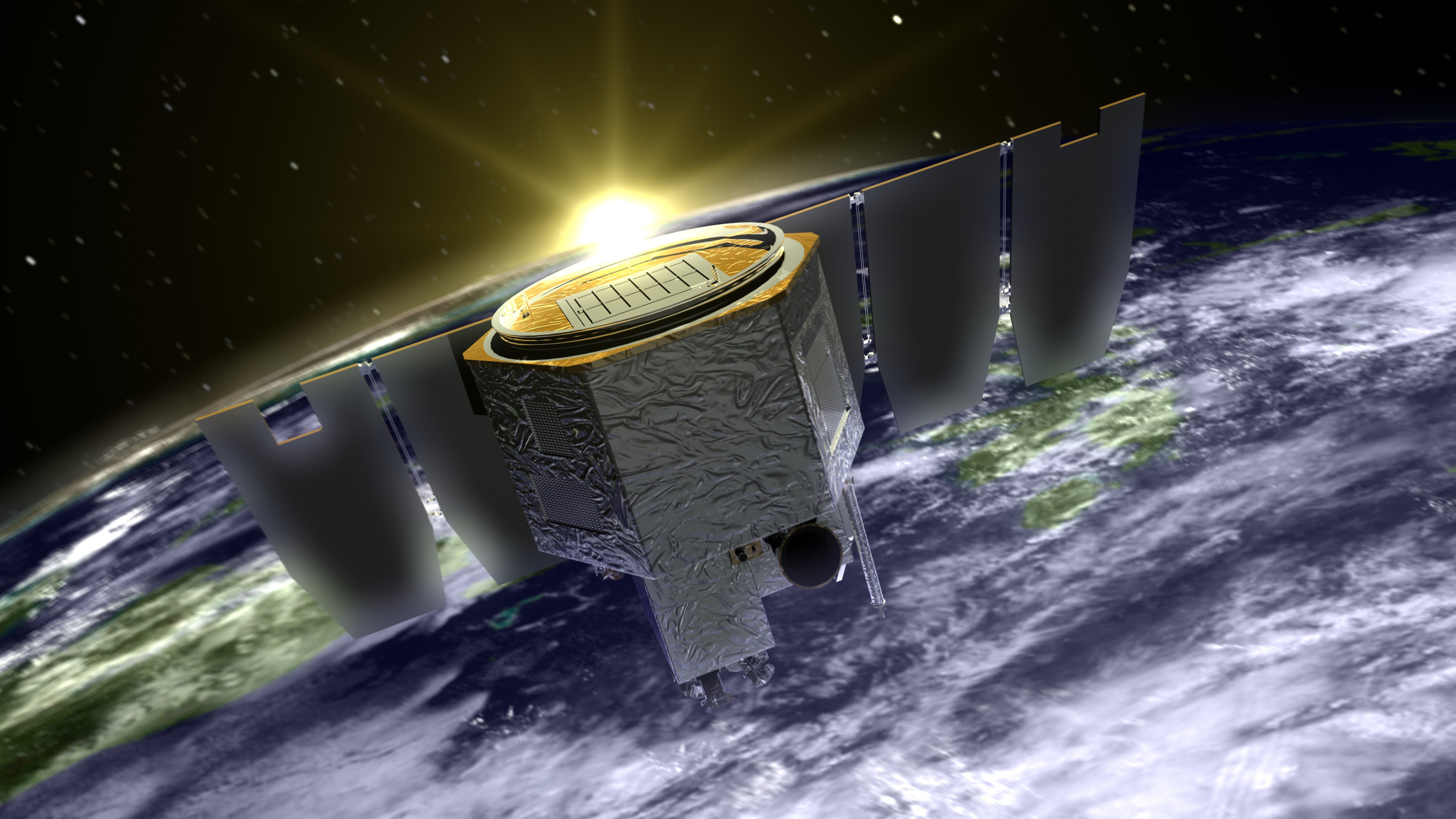
After 16 years studying Earth’s greatest clouds for the advantage of humankind– polar mesospheric clouds– from its orbit some 350 miles in the air, NASA’s Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or GOALobjective has actually concerned an end.
Slated for a two-year objective, AIM was extended various times due to its high science return. While AIM has actually dealt with difficulties throughout the years– from software application missteps to hardware problems– an exceptionally devoted group kept the spacecraft running for a lot longer than anybody might have prepared for. On March 13, 2023, the spacecraft’s battery stopped working following a number of years of decreasing efficiency. Numerous efforts to keep power to the spacecraft were made, however no additional information might be gathered, so the objective has actually now ended.
“AIM was committed to studying the climatic area that surrounds in between our environment and area,” stated AIM objective researcher Diego Janches, of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “AIM’s assistance understanding this area has actually been of crucial significance to supplying insights on how the lower environment impacts area weather condition.”
Called night-shining or noctilucent clouds, they are seen at golden in the summertime, usually at high latitudes near the North and South Poles. Before the objective, researchers understood these kinds of clouds differed with latitude, season, and solar activity, however didn’t understand why. This objective was released to comprehend the variations and research study why the clouds form and their links to environment modification by determining the thermal, chemical, and other homes of the environment in which the clouds form.
“NASA’s AIM has actually been an extremely effective objective,” stated Scott Bailey, AIM principal private investigator and teacher at Virginia Tech. “It has actually addressed core concerns that have actually assisted us comprehend how noctilucent clouds and climatic gravity waves differ in time and place.”
Throughout the years, AIM made lots of huge discoveries. Information from the objective has actually so far resulted in almost 400 peer-reviewed publications. This consists of findings on how these clouds can be produced by meteor smoke and water vapor from rocket exhausthow occasions near Earth’s surface area can activate modifications in the clouds, and how ice high in the environment can trigger strange radar echoeswhich are developed in specific areas of the environment throughout the summer season.
As the objective advanced, researchers understood AIM’s information might likewise be utilized to study wavinesses in the air called climatic gravity waves. These waves transfer momentum and energy as they take a trip through the environment. They connect weather condition occasions at Earth’s surface area with climatic disruptions that happen far from the preliminary occasion, consisting of in the uppermost part of the environment where they can interfere with GPS signals.
“We’ve had lots of problems, however we’ve still gotten an amazing quantity of information from AIM due to the fact that of our actually outstanding, brave, and hardworking group that comes through each time,” Bailey stated.
Goal’s very first difficulties began just months after launch in 2007, when the telecommunication receiver began to malfunction periodically. With a creative usage of radio signals, the group had the ability to reprogram the spacecraft to interact in Morse code, which permitted it to preserve interactions even after the receiver quit working. While interaction with the spacecraft ended up being countless times slower than prepared, AIM was still able to make its measurements and send out home 99% of the information it gathered.
Quickly afterwards, the spacecraft once again came across a mission-threatening concern. The spacecraft consistently sent itself into safe mode, which efficiently closed down the spacecraft and needed a lengthy series of jobs to reboot. Once again, the engineers were able to publish brand-new software application to the spacecraft to prevent the problem and keep AIM practical. The brand-new software application spot has actually avoided over a thousand such events on the spacecraft considering that.
In 2019, AIM’s battery began to decrease, however through excellent effort and resourcefulness, the objective operations group kept the battery power, allowing the spacecraft to continue returning information. In early 2023, the battery experienced a considerable drop-off in efficiency which suggested the spacecraft might sporadically get commands or gather information. This hardware problem was not one that might be fixed from another location, and the satellite lastly stopped gathering information in March 2023.
“We’re distressed to see AIM reach completion of its life time, however it’s been incredible for how long it has actually lasted,” Bailey stated. “It’s offered us more information and insight into noctilucent clouds and climatic gravity waves than we might ever have actually expected.”
The spacecraft has actually seen its last night-shining clouds, researchers will continue to study AIM’s information for years to come. When it comes to the spacecraft itself, it will gradually lose orbital height and burn up upon environment re-entry in 2026.
“There are still gigabytes upon gigabytes of AIM information to study,” stated Cora Randall, AIM deputy primary detective and senior research study researcher at the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, Colorado. “And as our designs and computational abilities continue to enhance, individuals will make much more discoveries utilizing the AIM datasets.”