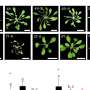
A hereditary suppressor screen recognizes RdDM to be the significant path for repeat expansion-induced epigenetic silencing.aPhenotypes (signified by their initial screen identifiers)of the separated suppressors compared to Bur-0. The irregularly impaired leaves are marked by white arrows in the Bur-0 wild type. Scale bars, 2 cm.bRelative IIL1expression levels in hereditary suppressors recognized through the hereditary screen. The numbers represent the initial screen identifiers, and the matching genes determined after cloning are revealed listed below. Typical expression levels based upon 3 biological duplicates for each line( other than for Bur-0 and fug1wheren= 5 and 4, respectively)are revealed. Asterisks (*)signify private information points.Pworths are based upon a one-way analysis of difference with Tukey’s post hoc test, and lines with various letters are considerably various from each other(P< 0.05). Mistake bars represent s.e.m.cAn example of SHOREmap analysis with44-2determines an anomaly inPol VHigh-frequency alleles(> 0.85)are colored red, and red crosses reveal the putative causal alleles. Credit:Nature Plants(2024). DOI: 10.1038/ s41477-024-01672-5
Monash University biologists have actually clarified the elaborate molecular systems that are accountable for gene silencing caused by broadened repeats in a worldwide research study released today inNature Plants
This phenomenon has actually been connected to a variety of genetic diseases, consisting of Friedreich’s ataxia in human beings, and triggers development irregularities in plants such as Arabidopsis thaliana.
The research study intended to comprehend the system by which bigger repeats trigger epigenetic silencing, a vital treatment for managing gene expression.
Finding unique elements that are essential for this silencing procedure was achieved by the scientists utilizing a plant design that provides the signs of development problems at greater temperature levels however not at lower temperature levels.
SUMO protease FUG1, histone reader AL3, and chromodomain protein LHP1 were recognized as the 3 crucial stars, according to the research study.
“These proteins come together to produce an important module needed for epigenetic silencing caused by repeat growth,”stated lead research study author Dr. Sridevi Sureshkumar, who heads the Genetics at the Core Research Group at the Monash University School of Biological Sciences.
” Our research study exposes the essential function that these proteins play in managing gene silencing that is activated by broadened repeats,” Dr. Sureshkumar stated.
“The awareness of these systems not just adds to the development of our understanding of plant biology however likewise uses insights into illness that impact people,”she stated.
Throughout the course of the research study, modern-day hereditary screening approaches and yeast two-hybrid tests were made use of in order to figure out that FUG1, an uncharacterized SUMO protease, is a substantial individual in epigenetic silencing. Following more analysis, it was revealed that FUG1 engages with AL3, which is a histone reader that is understood to bind to specific histone marks that belong to efficient gene expression
In addition, the scientists discovered that the AL3 protein engages with LHP1, which is a chromodomain protein that contributes in the dissemination of limiting histone marks. The turnaround of gene silencing and the suppression of repeat expansion-associated signs were both caused by the loss of function of any among these parts throughout the experiment.
“These findings highlight the significance of post-translational modifiers and histone readers in epigenetic guideline,” Dr. Sureshkumar stated.
“Our research study leads the way for additional research study into the function of these proteins in numerous biological procedures and human illness,” she stated.
“The findings not just present possible effects for human health however likewise add to our understanding of plant biology, which is currently advanced.”
Dr. Sureshkumar, who led this global research study including Institutions in the UK, China, Canada, India, and Australia, stated that international cooperation assisted them make development throughout varied elements of this research study.
Dr. Sureshkumar stated this research study might possibly be a path for the advancement of unique healing strategies that target epigenetic dysregulation in individuals who struggle with genetic diseases.
More info:
Sridevi Sureshkumar et al, SUMO protease FUG1, histone reader AL3 and chromodomain protein LHP1 are important to duplicate expansion-induced gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana,Nature Plants(2024 ). DOI: 10.1038/ s41477-024-01672-5
Citation: Uncovering crucial gamers in gene silencing: Insights into plant development and human illness (2024, April 19) recovered 19 April 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-uncovering-key-players-gene-silencing.html
This file goes through copyright. Apart from any reasonable dealing for the function of personal research study or research study, no part might be replicated without the composed consent. The material is attended to info functions just.